Indirect Cooling Systems and Secondary Refrigeration
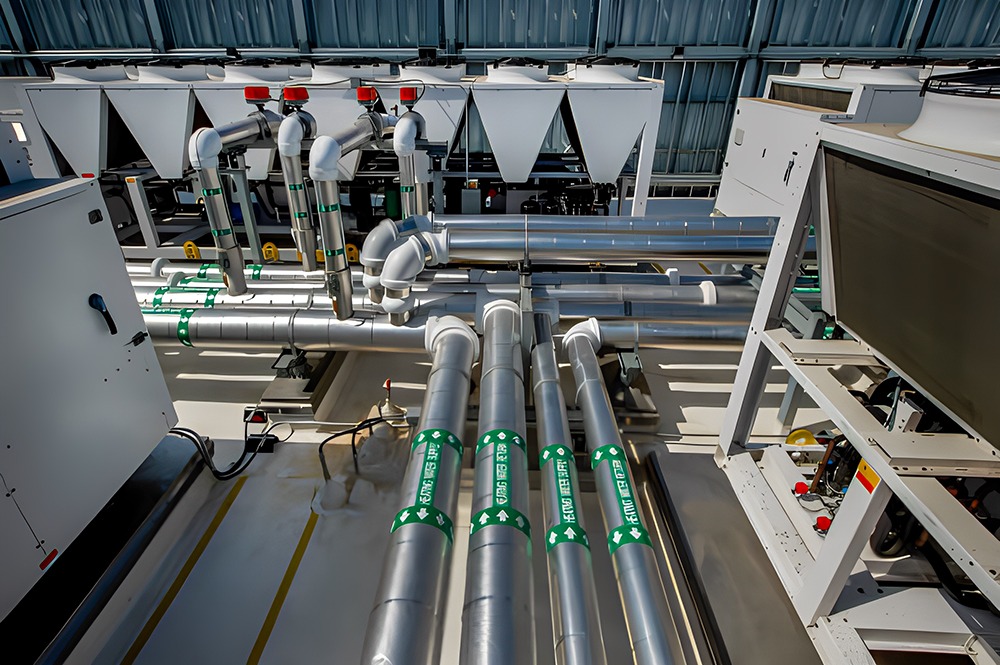

Transferring cold and protection against corrosion
The difference between direct cooling systems and indirect cooling systems, also known as secondary refrigeration, resides in the physical separation between the primary circuit, where the cold is generated, and the secondary system, where cooling takes place. The cold generated in the primary circuit is transported by the heat transfer fluid to the place where the products need to be cooled. Temperatures for this application can vary from -40 °C to 40 °C.
In indirect refrigeration systems, heat transfer fluids have two basic functions:
- To transfer the cold: the coolant in indirect cooling systems must remain fluid at all prevailing temperatures in the system, and the viscosity should preferably be as low as possible.
- To protect the system against corrosion: compared to other applications, corrosion protection at low temperatures requires a different set of inhibitors and a different protection mechanism. Our products are designed to offer maximum protection under all conditions.
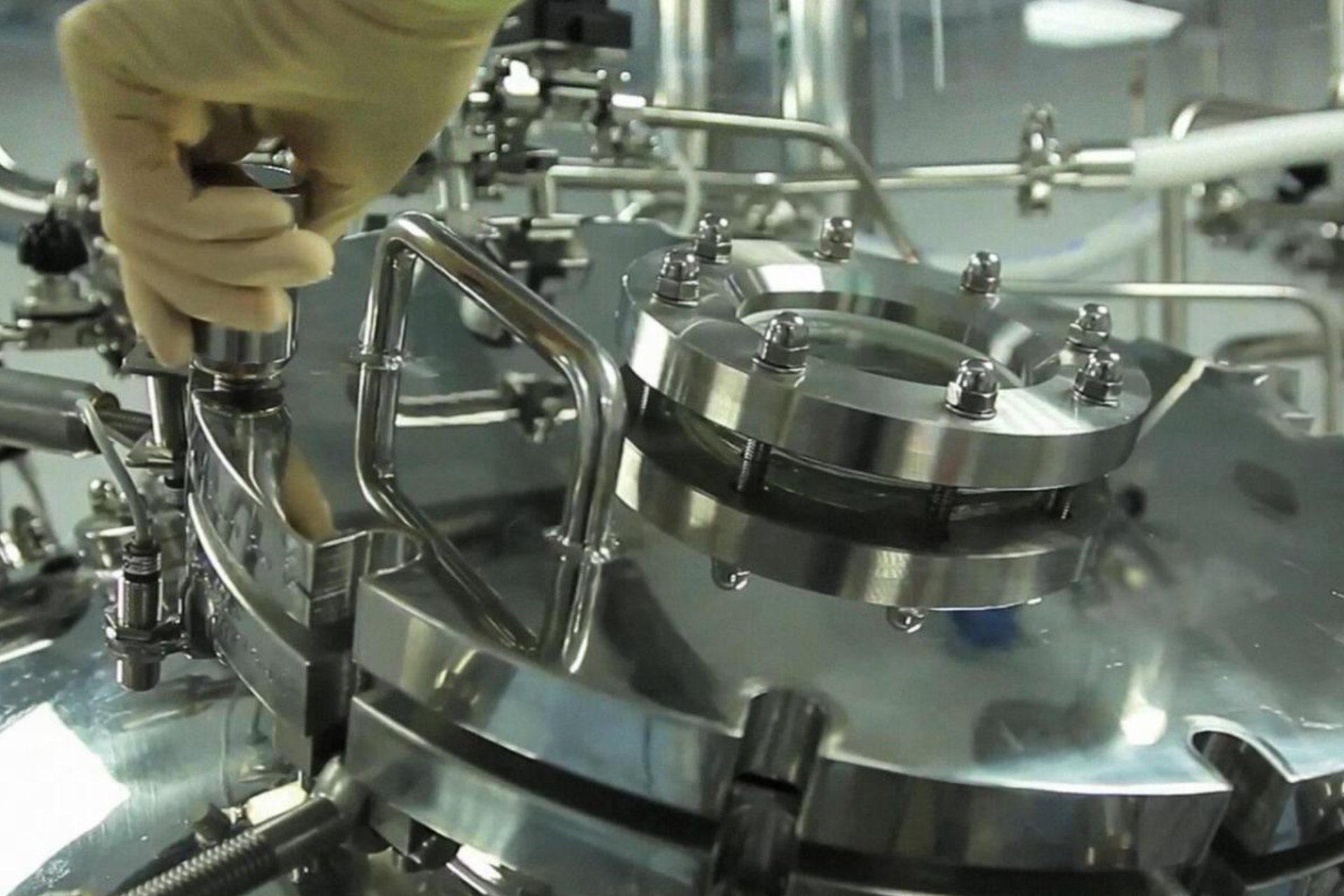

Benefits of indirect refrigerant systems:
- Minimal amount of refrigerant
- Reduced risk of leakage of the primary refrigerant
- Reduced system size
- Less severe demands on piping and pumps
- Fewer legally mandatory maintenance and checking operations for smaller primary cooling circuits
- Simpler to modify, which makes it extremely attractive for production processes requiring flexibility
- Transporting refrigerant over a long distance is avoided, as the secondary fluid can easily be carried away from the system and cooled at a convenient distance

Examples of application areas:
- Indirect systems in supermarkets:
In supermarkets, the cold needs to be transported to a variety of fresh and frozen displays in an effective, safe and economical way. All the cooling effect required is produced in the machine room, far from the display cases, resulting in high flexibility and a reduced risk of leakage. A heat recovery system, also situated in the machine room, can provide heating for the supermarket when required. Consequently, the use of unwanted refrigerant such as ammonia in a public place is avoided, although it can still be used in the primary system. -
Medical Devices and Pharmaceutical Processing
-
Power Generation and Industrial Utilities
-
Polymer Manufacture
-
Food and Beverage Production

More Applications

Hot Water Heating Systems and Air Conditioning
Hot water heating systems and air conditioning are commonly used to ensure comfortable temperatures in buildings.
More Details
Heat Pump Systems
Reversing the natural heat flow direction. Heat flows naturally from a higher to a lower temperature. Heat pumps, however, are able to reverse this flow in the other direction.
More Details
Liquid Coolants for Data Centres And Electronics
Cooling is an essential aspect to consider when it comes to computing systems and electronic applications.

Process Heating and Cooling
In the chemical industry, many processes require either cooling or heating. The temperature range of applications can widely vary.
More Details
Indirect Contact Freezing
Freezing food is probably the gentlest method of food preservation. Freezing prevents food from spoiling by inhibiting micro-organic and enzymatic action.

