Process Heating and Cooling
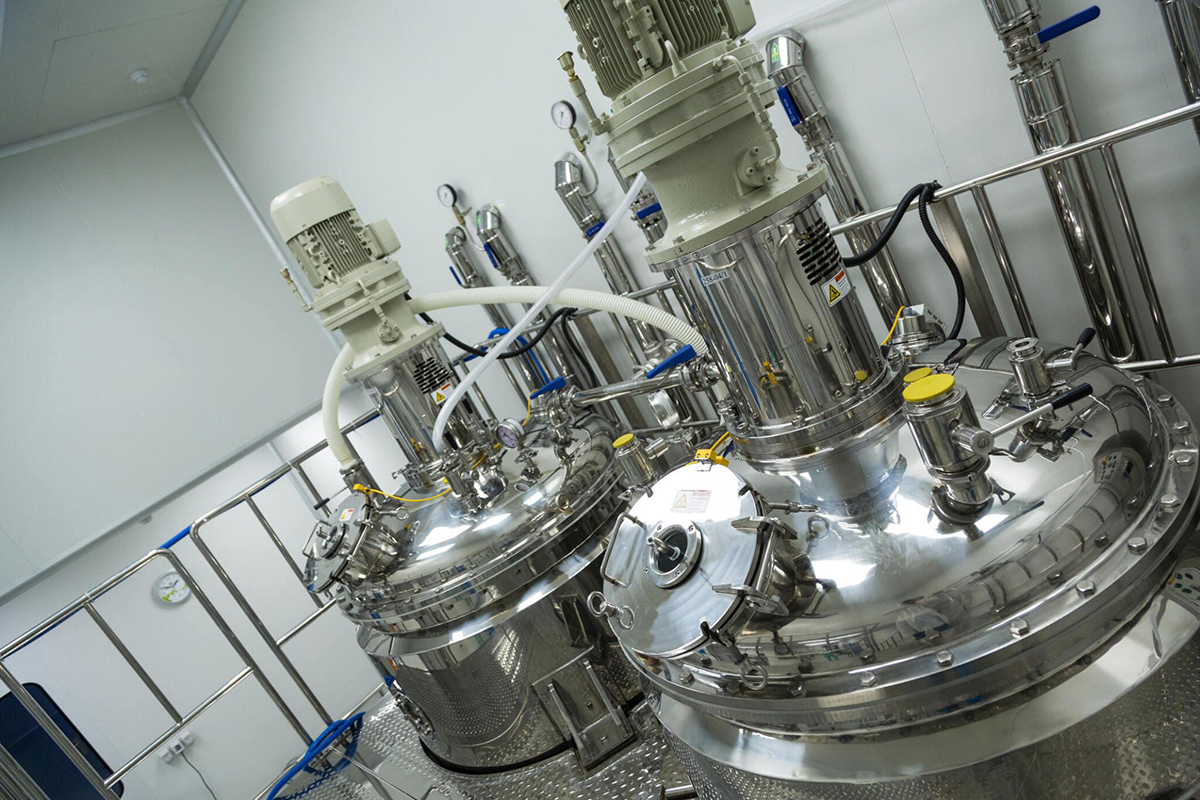

In the chemical industry, many processes require either cooling or heating. The temperature range of applications can widely vary.
Temperatures varying from -120 °C to +150 °C
In most cases, the heat transfer fluid will only be used at one temperature. However, in some applications the same fluid is used at different steps of the process and at different temperatures (e.g. reaction processes where cooling is needed during the exothermic reaction and followed by heating to remove water during the crystallisation step).
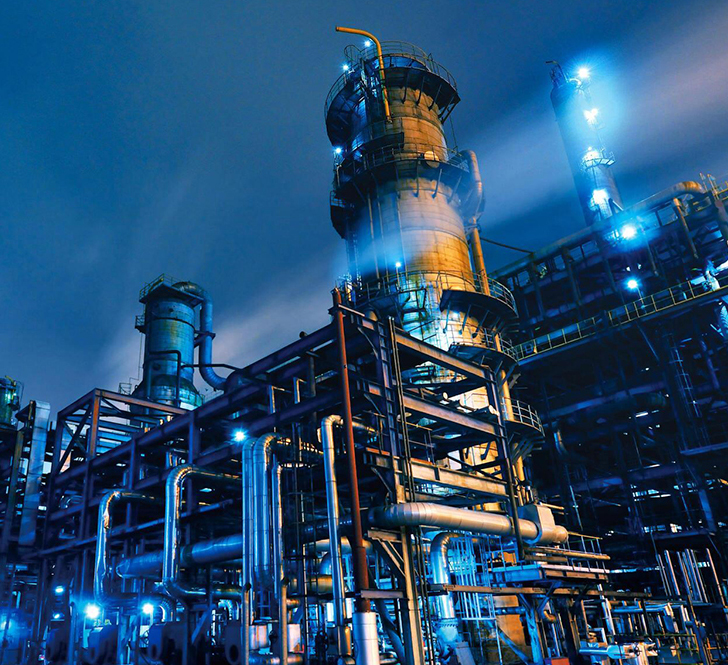

Process heating and cooling systems utilise a heater or chiller in combination with thermal oil, water, glycol, or silicon thermal fluids. The system warms or cools the fluid of choice before continuously recirculating it through the system, transferring indirect heat to the appropriate process systems, machinery, and materials. Thermal fluid heating systems provide centralised indirect heat so the heater and the heated object never directly touch, one of the many benefits compared to direct-fired heating systems.
Thermal fluid systems utilise two loops to control the requirements of each of its heat consumers.
- The primary loop provides thermal fluid to one or more consumers at a consistent flow rate and temperature, whatever the return temperature. This loop is made up of a heater, drain and expansion tanks, and a single or multiple circulation pumps.
- The secondary loop thermal fluid systems can have single or multiple secondary loops. Secondary loops help meet consumer demands by drawing thermal energy from the fluid at its necessary flow rate and temperature.
More Applications

Hot Water Heating Systems and Air Conditioning
Hot water heating systems and air conditioning are commonly used to ensure comfortable temperatures in buildings.
More Details
Indirect Cooling Systems and Secondary Refrigeration
The difference between direct cooling systems resides in the physical separation between the primary circuit and the secondary system
More Details
Heat Pump Systems
Reversing the natural heat flow direction. Heat flows naturally from a higher to a lower temperature. Heat pumps, however, are able to reverse this flow in the other direction.
More Details
Liquid Coolants for Data Centres And Electronics
Cooling is an aspect to consider when it comes to computing systems and electronic applications.

Indirect Contact Freezing
Freezing food is probably the gentlest method of food preservation. Freezing prevents food from spoiling by inhibiting micro-organic and enzymatic action.

